Using the CodeQL model editor¶
Note
The CodeQL model editor and CodeQL model packs are currently in beta and subject to change. During the beta, model packs are supported only by Java/Kotlin and C# analysis. To use this beta functionality, install the latest version of the CodeQL extension for Visual Studio Code.
You can view, write, and edit CodeQL packs in Visual Studio Code using the CodeQL extension. The model editor is designed to help you model external dependencies of your codebase that are not supported by the standard CodeQL Libraries.
About the CodeQL model editor¶
The CodeQL model editor guides you through modeling the calls to external dependencies in your application or fully modeling all the public entry and exit points in an external dependency.
When you open the model editor, it analyzes the currently selected CodeQL database and identifies where the application uses external APIs and all public methods. An external (or third party) API is any API that is not part of the CodeQL database you have selected.
The model editor has two different modes:
- Application mode (default view): The editor lists each external framework used by the selected CodeQL database. When you expand a framework, a list of all calls to and from the external API is shown with the options available to model dataflow through each call. This mode is most useful for improving the CodeQL results for a specific codebase.
- Dependency mode: The editor identifies all of the publicly accessible APIs in the selected CodeQL database. This view guides you through modeling each public API that the codebase makes available. When you have finished modeling the entire API, you can save the model and use it to improve the CodeQL analysis for all codebases that use the dependency.
Displaying the CodeQL model editor¶
- Open your CodeQL workspace in VS Code, for example, the
vscode-codeql-starterworkspace. If you haven’t updated theqlsubmodule for a while, update it frommainto ensure that you have the queries used to gather data for the model editor. - Open the CodeQL extension and select the CodeQL database that you want to model from the “Databases” section of the left side pane.
- In the left side panel, expand the “CodeQL method modeling” section and click Start modeling to display the model editor. Alternatively, use the command palette to run the “CodeQL: Open Model Editor (Beta)” command.
- The CodeQL model editor runs a series of telemetry queries to identify APIs in the code and the editor is displayed in a new tab.
- When the telemetry queries are complete, the APIs that have been identified are shown in the editor.
Tip
The “CodeQL method modeling” section is a view that you can move from the primary sidebar to the secondary sidebar, when you want more space while you are modeling calls or methods. If you close the view, you can reopen it from the “Open Views” option in the View menu.
Modeling the calls your codebase makes to external APIs¶
You typically use this approach when you are looking at a specific codebase where you want to improve the precision of CodeQL results. This is useful when the codebase uses frameworks or libraries that are not supported by CodeQL and if the source code of the framework or library is not included in the analysis.
This section uses an open source Java project called “sofa-jraft” as an example. The experience of modeling calls to external APIs written in other static languages is similar.
Select the CodeQL database that you want to improve CodeQL coverage for.
Display the CodeQL model editor. By default the editor runs in application mode, so the list of external APIs used by the selected codebase is shown.

Click to expand an external API and view the list of calls from the codebase to the external dependency.
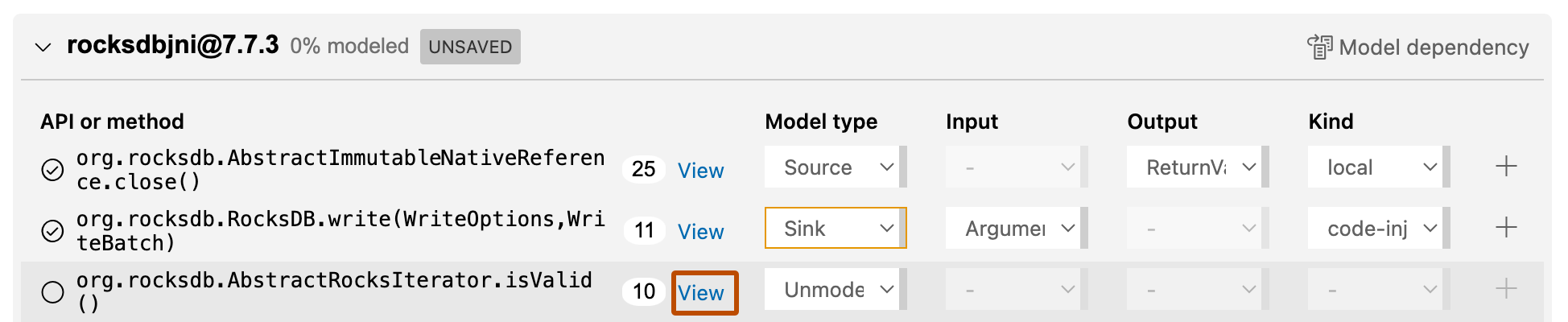
Click View associated with an API call or method to show where it is used in your codebase.
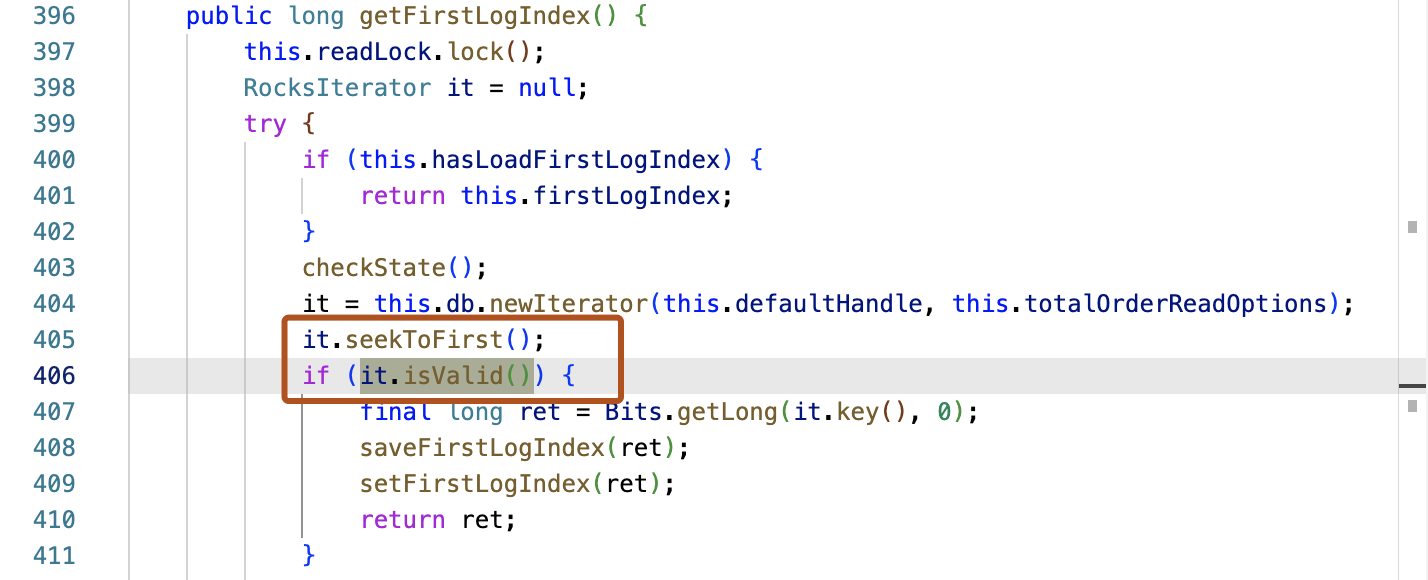
The file containing the first call from your codebase to the API is opened and a “CodeQL methods usage” view is displayed in the VS Code Panel (where the “Problems” and “Terminal” views are usually displayed). The “CodeQL methods usage” view lists of all the calls from your code to the API, grouped by method. You can click through each use to decide how to model your use of the method.
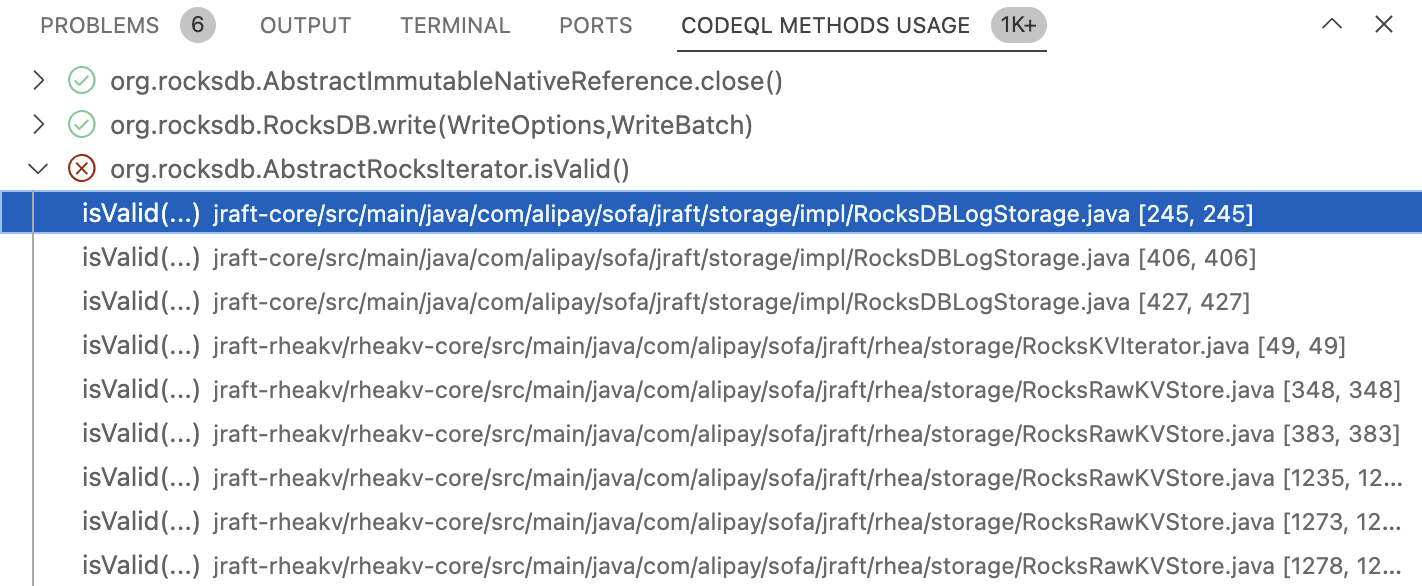
When you have determined how to model your use of the method, you can define the Model type in the “CodeQL method modeling” tab of the CodeQL extension. This change is automatically reflected in the main model editor.
The remaining fields are updated with available options:
- Source: choose the Output element to model.
- Sink: choose the Input element to model.
- Flow summary: choose the Input and Output elements to model.
Define the Kind of dataflow for the model.
When you have finished modeling, display the main model editor and click Save all or Save (shown at the bottom right of each expanded list of methods). The percentage of methods modeled in the editor is updated.
The models are stored in your workspace at .github/codeql/extensions/<codeql-model-pack>, where <codeql-model-pack> is the name of the CodeQL database that you selected. That is, the name of the repository, hyphen, the language analyzed by CodeQL. For more information, see “Using CodeQL model packs with code scanning”.
The models are stored in a series of YAML data extension files, one for each external API. For example:
.github/codeql/extensions/sofa-jraft-java # the model pack directory
models
jmh-core.model.yml # models calls to jmh-core@1.20
rocksdbjni.model.yml # models calls to rocksdbjni@7.7.3
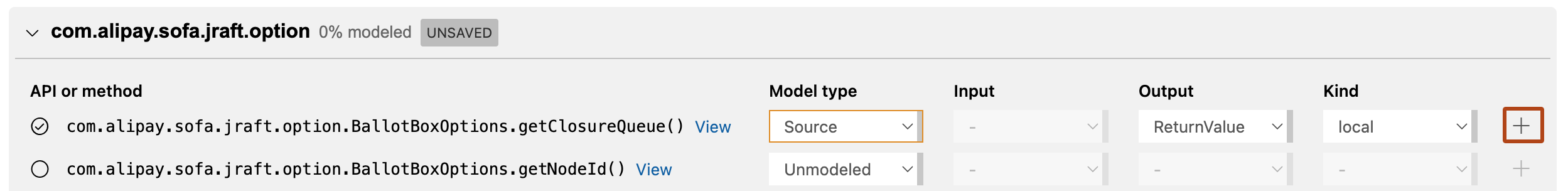
Modeling the public API of a codebase¶
This section uses an open source Java project called “sofa-jraft” as an example. The experience of modeling the public API written using other static languages is similar.
You typically use this method when you want to model a framework or library that your organization uses in more than one codebase. Once you have finished creating and testing the model, you can publish the CodeQL model pack to the GitHub Container Registry for your whole organization to use.
Select the CodeQL database that you want to model.
Display the CodeQL model editor. By default the editor runs in application mode. Click Model as dependency to display dependency mode. The screen changes to show the public API of the framework or library.

Click to expand a package and view the list of available methods.
Click View associated with a method to show its definition.
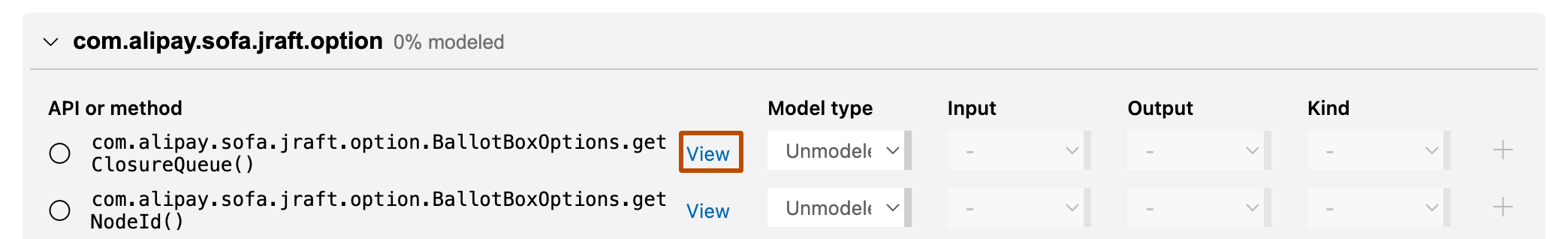
When you have determined how to model the method, define the Model type.
The remaining fields are updated with available options:
- Source: choose the Output element to model.
- Sink: choose the Input element to model.
- Flow summary: choose the Input and Output elements to model.
Define the Kind of dataflow for the model.
When you have finished modeling, click Save all or Save (shown at the bottom right of each expanded list of calls). The percentage of calls modeled in the editor is updated.
The models are stored in your workspace at .github/codeql/extensions/<codeql-model-pack>, where <codeql-model-pack> is the name of the CodeQL database that you selected. That is, the name of the repository, hyphen, the language analyzed by CodeQL. For more information, see “Using CodeQL model packs with code scanning”.
The models are stored in a series of YAML data extension files, one for each public method. For example:
.github/codeql/extensions/sofa-jraft-java # the model pack directory
models
com.alipay.sofa.jraft.option.model.yml # models public methods in package
com.alipay.sofa.jraft.rhea.options.model.yml # models public methods in package
The editor will create a separate model file for each package that you model.
Modeling methods with multiple potential flows¶
Some methods support more than one data flow. It is important to model all the data flows for a method, otherwise you cannot detect all the potential problems associated with using the method. First you model one data flow for the method, and then use the + button in the method row to specify a second data flow model.
Testing CodeQL model packs in VS Code¶
You can test any CodeQL model packs you create in VS Code by turning the “use model packs” setting on and off. This method works for both databases and for variant analysis repositories.
- To run queries on a CodeQL database with any model packs that are stored within the
.github/codeql/extensionsdirectory of the workspace, update yoursettings.jsonfile with:"codeQL.runningQueries.useExtensionPacks": "all", - To run queries on a CodeQL database without using model packs, update your
settings.jsonfile with:"codeQL.runningQueries.useExtensionPacks": "none",
If your model is working well, you should see a difference in the results of the two different runs. If you don’t see any differences in results, you may need to introduce a known bug to verify that the model behaves as expected.
Using CodeQL model packs with code scanning¶
There are two methods for using CodeQL model packs with code scanning:
- Copy the model pack directory into the
.github/codeql/extensionsdirectory of the repository. It will automatically be used by all future code scanning analysis for the repository (default setup or advanced setup). - Publish the model pack to the GitHub Container Registry as a CodeQL model pack. This can be downloaded and used by advanced setup for code scanning or by the CodeQL CLI running in an external CI system.
For more information, see the following articles on the GitHub Docs site:
- Default setup of code scanning: Extending CodeQL coverage with CodeQL model packs in default setup
- Advanced setup of code scanning: Extending CodeQL coverage with CodeQL model packs
- CodeQL CLI setup in external CI system: Using model packs to analyze calls to custom dependencies